Export means the total production of goods and services nationwide over a period of time – the sum of its domestic product. This term can refer to any activity, power, commodity, or service produced by a person, company, industry, or machine. In the computer world, refers to any data that has been processed and transmitted by a similar computer or device. Anything we watch on our computer monitor comes out.
It may also refer to any electrical device where power (or data) leaves the system.
In web design – HTML – the <output> tag is used to represent the result of a calculation (like the one created in the text) or the result of a user action.
In making a contract, this term refers to the desired result from a contractor or project. An exit contract is an agreement in which every product of the manufacturer is sold to the consumer – both the manufacturer and the buyer are committed to selling and purchasing (respectively) the entire product.
According to the Financial Times Glossary, the result is:
Until 1830, the term in English only referred to the trade in iron and coal. As a practice, it began to take on the meaning of ‘production’ in 1858.
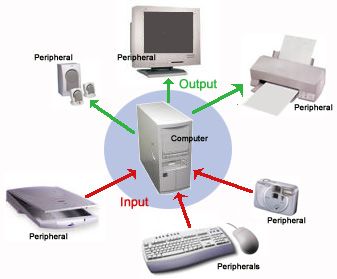
Input – Production – OutputInput refers to the raw materials, components and people you need to produce a finished product. For example, making a ship requires a variety of metals, plastics, wood, ropes, glass, electronic components, crew, welders, etc. Manufacturing is the process of making – that is when the materials and components are converted into a product. . The result is a production result – it usually refers to how much is produced.
Output in Economics
In economics, output is the total amount of goods and services a person, company, industry, city, region or country, or the world produces in a particular period. In the field of ** macroeconomics, the concept of national exit is important.
** Macroeconomics is an economic sector that looks at major economic factors, such as national productivity, inflation, unemployment or interest rates – factors that affect or exist throughout the economy.
Annual Release Gap – SANA according to the Viable Opposition website, the latest US exit gap started in 2008 – the longest and deepest of the worst gaps since 1980. The negative gap rose in 2009, a level that has weakened for almost three decades. Economists predict that the gap will not reach zero until at least 2018. (Photo: taken at-3.bp.blogspot.com)
What makes a country rich is not how much it has, but how much it produces.
Calculation of gross domestic product (GDP) is the most common measure of a national product. Economists say their biggest challenge when using the GDP method is to ensure that one product is not counted twice or more.
The country’s GDP should be equal to the value of all the products and services the country produces. However, when you combine everything, you actually end up counting the same thing several times, at different stages of production.
For example, consider a tailor who buys a man’s suit material for $ 50. He then cuts and sews the fabric and touches the last of the suit. He then sold the suit for $ 150 – and the cost of turning the fabric into a suit was $ 100.
We can then say that you have added $ 100 to the product, instead of producing a good one that can cost $ 150. Increasing the sales value of the product, minus all non-labor costs in order to build the final product.
Economists can also avoid the issue of double counting by focusing only on the final sale, which includes all previous production stages.
Both methods are accurate, say economists. The second method, known as the cost method, is the most widely used method of calculating the GDP of many countries.
There is a great deal of risk in over-reporting on imports. If a US company buys a product made in Vietnam, these costs should not be included in the consumer costs of US GDP, because the product purchased is foreign. That is why imports are not included in the GDP calculation.
When we look at all these factors, we see that:
C = Consumer costs. I = Investment (Gross Fixed Capital Formation). G = Government Expenditure. X = Export. M = Imported.
Although the output is the total value generated, the results are the benefits your customers receive by purchasing your goods or using your services. In an article in the Harvard Business Review, Deborah Mills-Scofield writes: “Outcomes are important products, services, benefits, and revenue: What. The results create definitions, relationships, and differences: why. Outputs, such as income and profits, enable us to pay for results; but without consequences, there is no need for consequences. ”
Result Vs Result
Although the output is the total value generated, the results are the benefits your customers receive by purchasing your goods or using your services. In an article in the Harvard Business Review, Deborah Mills-Scofield writes: “Outcomes are important products, services, benefits, and revenue: What. The results create definitions, relationships, and differences: why. Outputs, such as income and profits, enable us to pay for results; but without consequences, there is no need for consequences. ”
Other related ‘exit’ terms
– Output Gap: the difference between the country’s current GDP and what that GDP would have been if production had been full – its potential GDP. If the country’s current GDP is $ 100bn, but its potential GDP – if productivity was full – is $ 110bn, the gap is $ 10bn or (minus) -10%. If the country gap is a positive number, like + 4%, it means it is producing more than its limited capacity.


