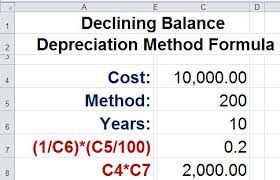
Depreciation is a common method used by businesses to expense the cost of their assets over time. This depreciation method allows businesses to track the changes in value of their assets and calculate their tax liability based on that change. In this article, we will discuss the Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method and how it works.
What Is the DMBS Method?
The double declining balance depreciation method is a conservative method used to calculate the depreciation expense on an asset. The method uses two periods of data, the first period being the initial cost of the asset and the second period being the estimated useful life of the asset. The depreciation expense is calculated as the difference between the initial and estimated useful lives.
How Does the DMBS Method Work?
The Double Declining Balance Method (DDBM) is a depreciation method used to calculate the depreciation expenses for fixed assets. The DDBM is a two-step method that uses the estimated useful life and declining balance method to calculate depreciation expenses.
The Advantages of the DMBS Method
The double declining balance depreciation (DMBS) method is a popular way to depreciate property. DMBS uses two steps to calculate depreciation: the first step calculates the estimated useful life of the property, and the second step calculates the depreciation rate over that period. The advantages of the DMBS method include its simplicity and accuracy.
The DMBS method is simple because it only requires two pieces of information: the estimated useful life of the property and the depreciation rate. The depreciation rate is easy to calculate because it is based on a fixed percentage of the estimated useful life. This makes DMBS an accurate method because it will always produce accurate results.
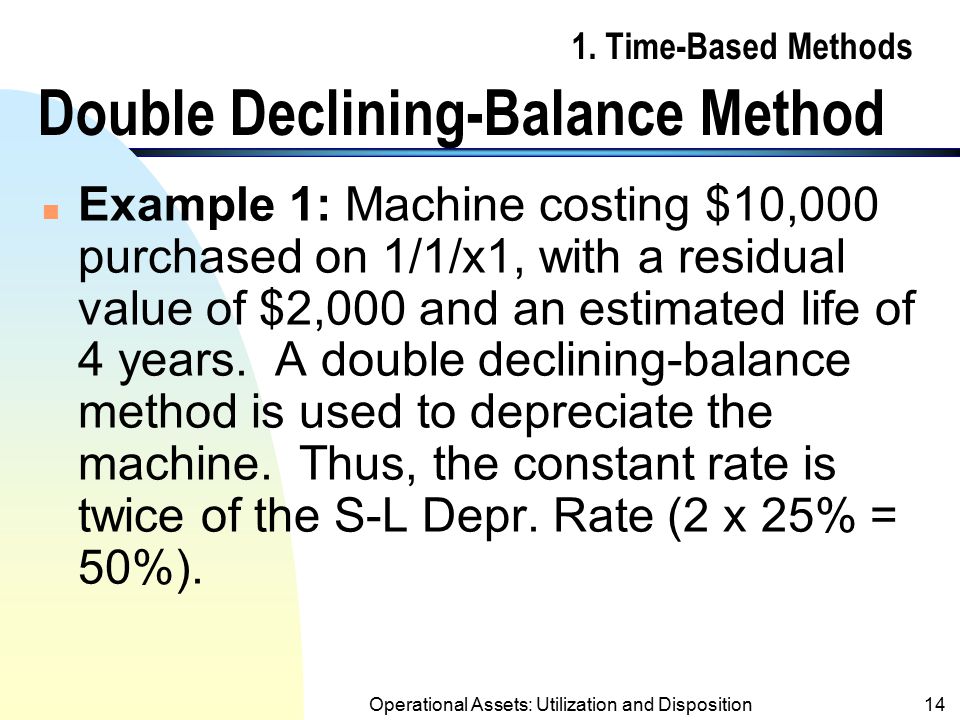
Another advantage of using DMBS is that it can be used for both new and old properties. This is because the depreciation rate for new properties is based on the estimated useful life for new properties, while the depreciation rate for older properties is based on a longer period of time (the estimated useful life for old properties). This allows property owners to use DMBS even if they don’t know their property’s estimated useful life yet.
Overall, DMBS is a reliable and accurate way to calculate depreciation. It is simple to use, and it can be used for both new
Disadvantages of the DMBS Method
The Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method (DDBM) is a depreciation method used by businesses to depreciate assets over time. However, there are several disadvantages to using this method.
First, the DDBM assumes that the asset will continue to produce income indefinitely. If the business expects the asset to produce less income in the future, then depreciation using the DDBM will be inaccurate.
Second, the DDBM requires businesses to track MACs and AMCs each year. This can be time-consuming and difficult to do.
Finally, the DDBM may not be appropriate for all types of assets. Certain assets, such as machinery and equipment, may be better suited for a straight-line depreciation method instead of the DDBM.
Conclusion
The Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method is a depreciation method that calculates the cost of an asset over two periods, with each period having a different rate. The first period is called the “base” period, and it has a lower rate than the second period, which is known as the “index” period. This depreciation method can be used to depreciate assets such as property, plant and equipment (PPE), intangible assets and goodwill.



